Japanese Automaker Warranty Expenses:
Honda's claims costs increased in 2024, after increasing warranty accruals in 2023 in response to a large global recall. However, all of the Japanese automakers saw their warranty costs increase in Japanese yen in 2024, due to the devaluation of the yen over the past few years.
The Japanese automakers use a fiscal year that spans from April 1 to March 31, and typically publish their annual reports, including their warranty expenses, over the summer. This week, we're taking a look at the product warranty expenses of Toyota, Honda, Nissan, Subaru, Suzuki, Mazda, Mitsubishi, and Isuzu, for the fiscal year that spanned April 1, 2024 to March 31, 2025.
These data are presented in Japanese yen (¥), as reported by each manufacturer. We will convert these amounts to U.S. dollars, using the IRS Yearly average currency exchange rates table, for our upcoming comparison of the warranty expenses of all of the worldwide automakers. However, since all of the manufacturers in this newsletter already report in the same currency, and the Japanese yen has significantly depreciated compared to the U.S. dollar over five-year data frame of the following charts, it makes more sense not to convert these data for this analysis.
Using the IRS table, here are average annual exchange rates for the value of $1 USD compared to Japanese yen: in 2024, $1 USD was worth roughly ¥150; in 2023, $1 was worth ¥140; in 2022, $1 was worth ¥130; in 2021, $1 was ¥110; and in 2020, $1 was worth about ¥107. However, keep in mind that the exchange rate has fluctuated quite a bit from month to month since 2022. These are just the annual averages calculated by the IRS, but other exchange rates could be considered equally valid.
Note that while all the Japanese automakers have a fiscal year from April to March, some refer to the fiscal year that spanned April 1, 2024 to March 31, 2025 as fiscal 2024, while others call it fiscal 2025. For our purposes, that year was fiscal 2024, and is labeled as 2024 in the following charts.
The Japanese Automakers
To create the following report, we perused the annual reports of the major Japan-based automakers: Toyota Motor Corp., Honda Motor Co., Nissan Motor Co., Subaru Corp., Suzuki Motor Corp., Mazda Motor Corp., Mitsubishi Motors Corp., and Isuzu Motors Ltd.
Toyota, Honda, and Nissan account for about three-quarters of the product revenue, and three-quarters of the product warranty expenses, of the Japanese automakers. Each of the three have their own luxury auto brands: Toyota has Lexus, Honda has Acura, and Nissan has Infiniti.
Mitsubishi Motors files a separate annual report from the larger parent conglomerate Mitsubishi Group, which is also an aerospace and heavy equipment manufacturer, defense contractor, the largest bank in Japan, and partial owner of the Japanese convenience store chain Lawson, through its many subsidiaries. Technically, Mitsubishi Motors is a subsidiary of Mitsubishi Corp., which in turn is a subsidiary of Mitsubishi Group. However, it gets more complicated, because Mitsubishi Motors is also partially owned by Nissan.
Mitsubishi, Nissan, and the European automaker Renault are each members of the Renault-Nissan-Mitsubishi Alliance, which grants each of the three automakers voting power in the other. The Renault-Nissan Alliance was formed in 1999, and in 2016, Nissan acquired 34% of Mitsubishi Motors, bringing the third manufacturer into the alliance.
In 2024, Honda and Nissan were in merger talks, to form what would have been the fourth-largest auto group by vehicle sales in the world, after Toyota, Volkswagen, and Hyundai. Mitsubishi and Renault would have been wrapped up in the merger as well, due to the alliance. The negotiations fell through in February 2025, and this merger of Japanese automakers will not proceed. However, it seems that the strategic partnership between the two automakers will continue.
Toyota, Subaru, Mazda, Suzuki, and Isuzu are united by small stakes of cross-ownership. Toyota fully owns smaller Japanese automakers Daihatsu and Hino, and 20% of Subaru, 5% of Mazda, 5% of Suzuki, and 5% of Isuzu. Toyota also has joint ventures with two state-owned Chinese automakers, FAW Group and GAC Group.
In terms of the warranty data they publish, Suzuki and Mazda both report the end-balance of the warranty reserve fund, but do not report total warranty claims paid or accruals made. We calculated estimates for these two warranty metrics, based on the reserve balances.
Isuzu and Nissan both report total warranty accruals and the reserve end-balance, and we fashioned estimates for the total warranty claims paid for each manufacturer.
From each annual report, we gathered three key warranty metrics: the amount of claims paid, the amount of accruals made, and the end-balance of the warranty reserve fund, according to which data were published.
In addition, we also gathered data on each manufacturer's total product (vehicle) sales revenue, and the total number of vehicles sold, and used these to calculate three additional warranty metrics: claims as a percentage of product revenue (the claims rate), accruals as a percentage of product revenue (the accrual rate), and accruals made per vehicle sold (in JPY).
Warranty Claims Totals
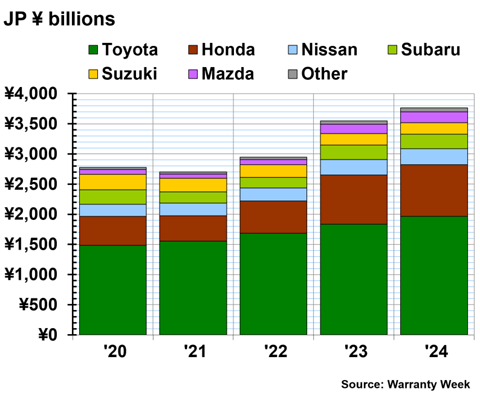
Figure 1 shows the total warranty claims paid by the Japanese automakers, from 2020 to 2024. Keep in mind that the data for Nissan, Suzuki, Mazda, and Isuzu (in the "Other" category) are estimates in Figure 1.
Figure 1
Japanese Auto Manufacturers
Claims Paid per Year
(in billions of ¥ yen, fiscal 2020-2024)
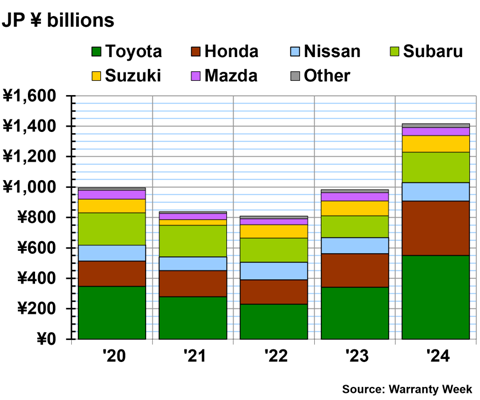
In fiscal 2024, Toyota paid ¥550 billion in warranty claims, a 61% increase from fiscal 2023. Honda paid ¥357 billion in claims in 2024, a 62% increase from the prior fiscal year.
Honda's increase in claims costs was paralleled by a drastic increase in the claims rate in fiscal 2024, as we will see in Figure 2. In December 2023, Honda announced the recall of 4.5 million vehicles globally, including 2.5 million in the United States, due to a fuel pump defect. We noticed that Honda increased accruals in fiscal 2023, likely in response to this recall, and it's not surprising that claims increased accordingly in the following fiscal year.
Toyota also had a few large recalls around the same time. In November 2023, the automaker recalled 1.8 million vehicles due to faulty 12-volt batteries, and in December 2023, 1.2 million vehicles were recalled worldwide due to an airbag issue.
Nissan paid ¥122 billion in claims in fiscal 2024, a 14% increase from fiscal 2023. Subaru paid ¥200 billion in claims, a 41% increase. Suzuki paid ¥109 billion, a 10% increase. Mazda paid ¥53 billion, a -3% decrease.
In the "Other" category, Mitsubishi paid ¥16 billion in warranty claims in fiscal 2024, a 21% increase from fiscal 2023. And Isuzu paid ¥9 billion in claims in fiscal 2024, a 45% increase from fiscal 2023.
Warranty Claims Rates
Figure 2 shows the annual warranty claims rates of the three largest Japanese automakers, Toyota, Honda, and Nissan, from 2020 to 2024.
Figure 2
Japanese Auto Manufacturers
Warranty Claims Rates
(as a percentage of sales, fiscal 2020-2024)
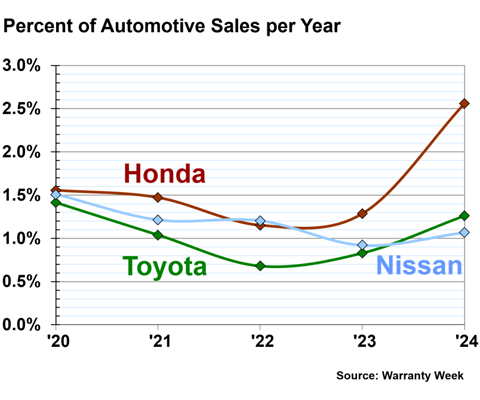
Honda's warranty claims rate doubled from fiscal 2023 to fiscal 2024. In fiscal 2023, Honda had a claims rate of 1.29%, and in fiscal 2024, the claims rate was 2.56%.
Toyota had a warranty claims rate of 1.26% in fiscal 2024. Nissan had a claims rate of 1.07% in fiscal 2024.
Warranty Accrual Totals
Figure 3 shows the total warranty accruals made by the top Japanese automakers, from 2020 to 2024. The data for Mazda and Suzuki are our estimates.
Figure 3
Japanese Auto Manufacturers
Accruals Made per Year
(in billions of ¥ yen, fiscal 2020-2024)
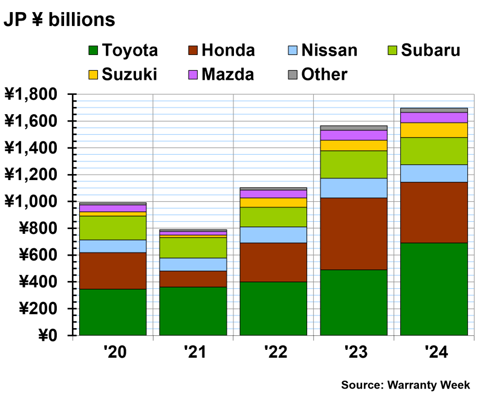
In fiscal 2024, Toyota set aside ¥690 billion in warranty accruals, a 41% increase from fiscal 2023. Honda set aside ¥455 billion in accruals, a -15% decrease from the prior fiscal year.
Nissan set aside ¥131 billion in warranty accruals in fiscal 2024, a -11% decrease from fiscal 2023. Subaru set aside ¥203 billion in accruals, the same amount as the prior fiscal year.
Suzuki set aside ¥109 billion in accruals in fiscal 2024, a 35% increase from fiscal 2023. Mazda set aside ¥77 billion in accruals in fiscal 2024, a 5% increase. Mitsubishi set aside ¥20 billion in accruals, a -14% decrease. And Isuzu set aside ¥12 billion in warranty accruals in fiscal 2024, a 16% increase from fiscal 2023.
Warranty Accrual Rates
Figure 4 shows the annual warranty accrual rates of Toyota, Honda, and Nissan, from 2020 to 2024.
Figure 4
Japanese Auto Manufacturers
Warranty Accrual Rates
(as a percentage of sales, fiscal 2020-2024)
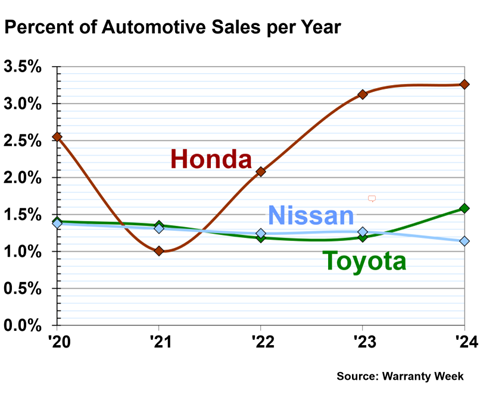
In fiscal 2024, Honda had a warranty accrual rate of 3.26%. Toyota had an accrual rate of 1.58%. And Nissan had a warranty accrual rate of 1.14%.
Accruals per Vehicle Sold
Global vehicle manufacturers always disclose the number of units they sell worldwide each year, so we calculate one additional warranty metric: the amount of warranty accruals per vehicle sold.
Of course, many of these manufacturers sell more than just passenger cars. Toyota also makes boats and buses. Honda makes motorcycles, planes, and generators. Nissan makes trucks and boat engines. Suzuki makes motorcycles, ATVs, and boat engines. And so on.
For the purposes of this exercise, let's assume that each manufacturer's main product line is passenger cars and light trucks, and that everything averages out to be comparable. It's not a huge leap; for example, 80% of Honda's product sales revenue comes from cars. So even if the expenses of its motorcycles or generators are different, it won't change the averages tremendously. And it's the best we can do with the publicly available data, in which warranty expenses are not segmented by product type.
Figure 5 shows the average warranty accruals per vehicle sold for six Japanese automakers, from 2020 to 2024.
Figure 5
Japanese Auto Manufacturers
Accruals Made per Vehicle Sold
(in ¥ yen, fiscal 2020-2024)
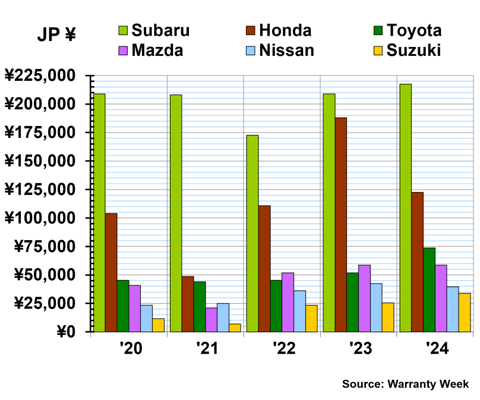
By far, Subaru sets aside the most in warranty accruals among the Japanese automakers. In fiscal 2024, Subaru set aside an average of ¥217,377 per vehicle sold, a 4% increase from fiscal 2023.
Honda set aside an average of ¥122,507 per vehicle sold in fiscal 2024, a -35% decrease from fiscal 2023.
Toyota set aside an average of ¥73,681 per vehicle sold in warranty accruals in fiscal 2024, a 42% increase from fiscal 2023's average of ¥51,887 per vehicle sold.
Mazda set aside an average of ¥58,673 in warranty accruals per vehicle sold in fiscal 2024, just about the same as the prior fiscal year. Nissan set aside an average of ¥39,573 per vehicle sold in fiscal 2024, a -7% decrease from fiscal 2023. And Suzuki set aside an average of ¥33,737 per vehicle sold in fiscal 2024, a 32% increase from fiscal 2023.
Warranty Reserve Balances
Figure 6 shows the warranty reserves held by each Japanese automaker at the end of each fiscal year, from 2020 to 2024. For the purposes of this newsletter, the end of fiscal 2024 was March 31, 2025, for each of these manufacturers.
Figure 6
Japanese Auto Manufacturers
Reserves Held at Year's End
(in billions of ¥ yen, fiscal 2020-2024)
At the end of fiscal 2024, Toyota held ¥1.966 trillion in its warranty reserve fund, a 7% increase from the balance at the end of 2023.
Honda held ¥858 billion in warranty reserves at the end of fiscal 2024, a 5% increase from the end of the prior fiscal year.
Nissan held ¥266 billion in warranty reserves at the end of fiscal 2024, a 3% increase from the end of the year prior. Subaru held ¥240 billion in reserves, a 1% increase. Suzuki held ¥190 billion in warranty reserves at the end of fiscal 2024, the same balance as at the end of fiscal 2023.
Mazda held ¥180 billion in warranty reserves at the end of fiscal 2024, a 15% increase from the end of fiscal 2023. Mitsubishi held ¥45 billion in reserves at the end of fiscal 2024, a 9% increase. And Isuzu held ¥17 billion in warranty reserves at the end of fiscal 2024, a 19% increase from the end of fiscal 2023.
Check out these newsletters on 2024 international auto warranty expenses: